Geo Textiles
Woven geotextiles are made with synthetic polymers that are woven together, the way that most fabrics are. These take longer to make, but also have a high tensile strength and load capacity. Basically, woven geotextiles are best when you need something very sturdy and durable.
Because of this, woven geotextiles are used for support and stabilization. For example, many roads and parking lots are built on top of a woven geotextile. The fabric holds the earth in place, preventing shifting or movement and creating a stable base for the construction on top of it. Woven textiles are also used to prop up shorelines or beaches that are at risk of collapsing or washing away, as well as to protect grounds from wind damage.
Overall, woven textiles are utilized for their strength. However, this high tensile strength makes the geotextiles relatively impermeable. This means that they will hold, rather than absorb or filter, water. So, if filtration is a big priority for your project, you may consider using something else.

Specifications
- G/m2 range:120g/m2~600g/m2
- Fabric breadth:4m~8m
Function
The woven geotextile is characterized by light weight, high strength, good integrity, convenient application, effective reinforcement and low cost.
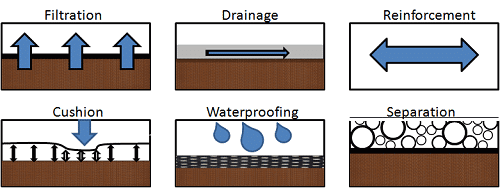
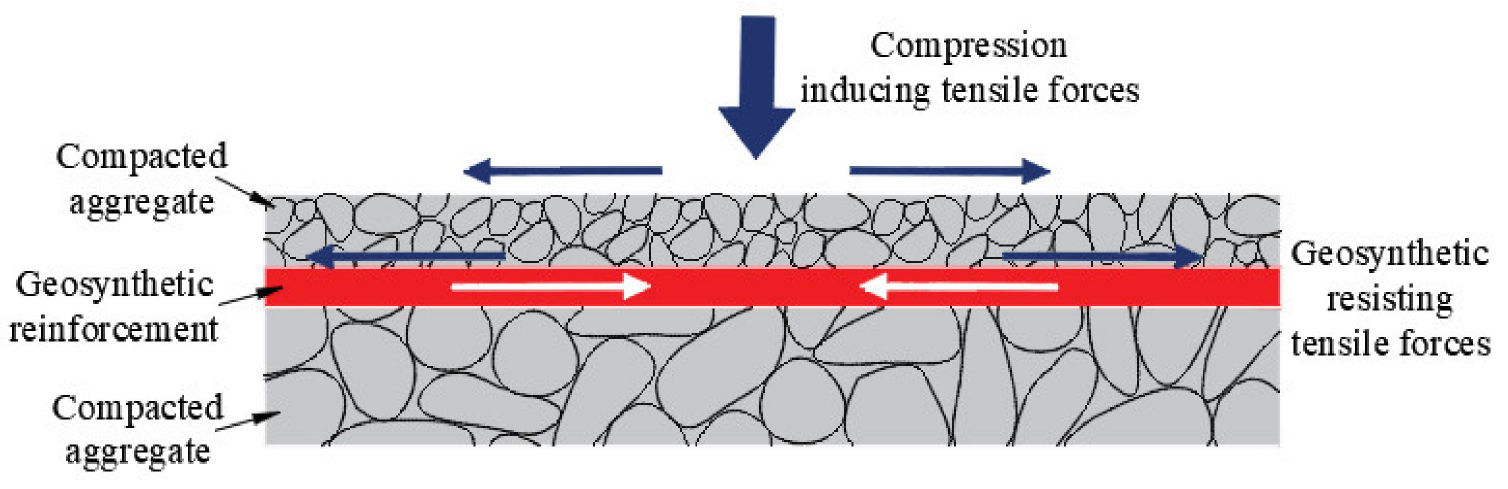
Re-inforcement
It can safely limit the excursion of civil work over long time of use and transfer or allocate the stress on soil over a larger area.
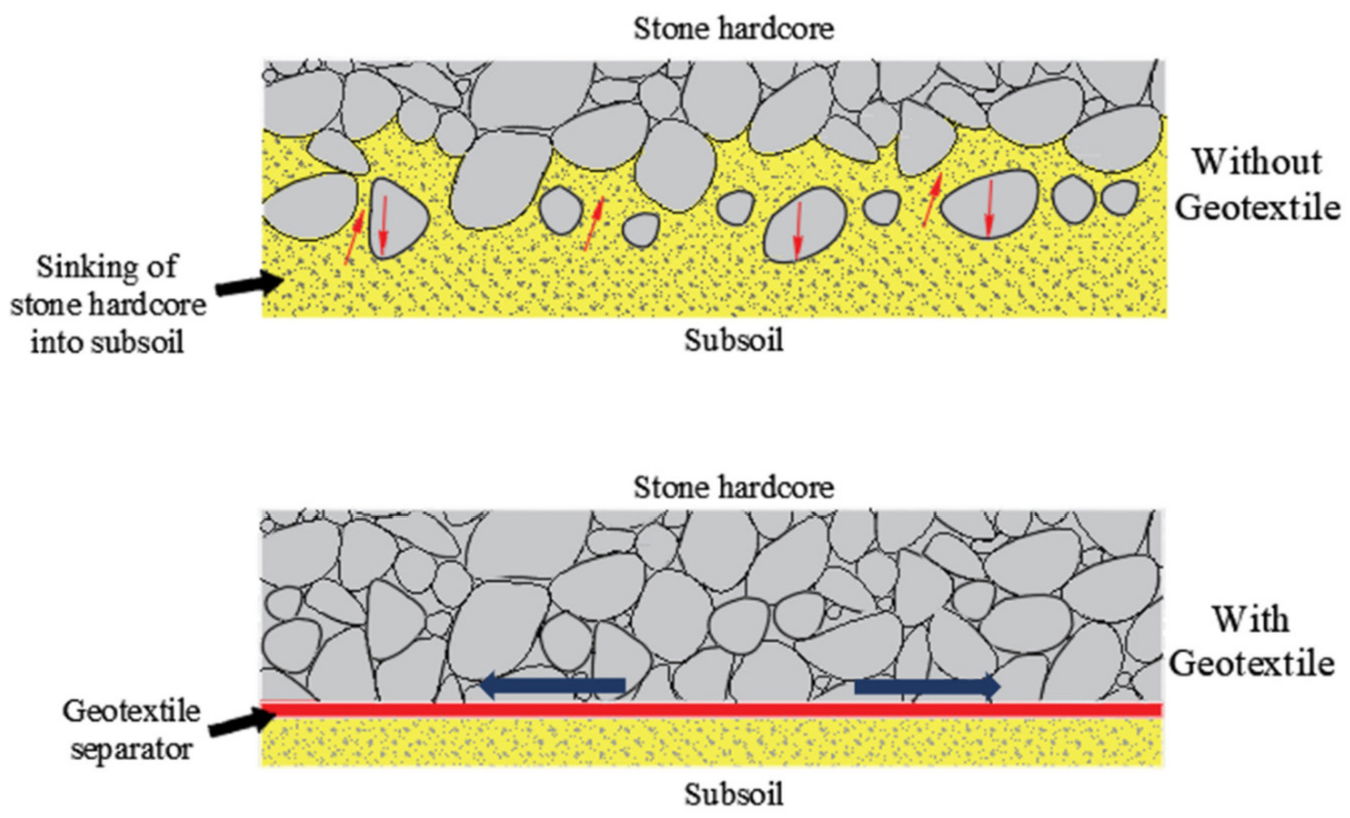
Separation
It can separate the civil work materials into stable interfaces and ensure them to function both individually and as a whole. The combined use of geotextile and geofilm can provide tension insulation between materials under different loads .The separation function of geotextiles refers to a geotextile can separate two kinds of materials with different properties, avoid mixing with each other, and lose the integrity and structural integrity of various materials. when stone aggregates are placed on fine-grained soil, both mechanisms will occur at the same time over time. One is that the fine soil in the lower layer tries to enter the void of the aggregate, thus destroying its drainage capacity; the other is that the aggregate in the upper layer tries to invade the fine soil, thus destroying the strength of the aggregate. This usually happens without the use of geotextiles.
In an internally unstable soil, seepage may cause the phenomenon of suffusion; the transport of fine particles by seepage flow is accompanied by a collapse of the soil structure. Because geotextiles have positive permeability and air permeability, they can be placed in the soil structure to allow the liquid in the soil to pass through and discharged, and play a role of soil conservation, which can effectively prevent the loss of soil particles, fine sand, and small stones in the upstream, prevent soil damage, and effectively avoid the phenomenon of suffusion. The mechanism is demonstrated. The filtration function of geotextiles is also widely used in geotechnical engineering.
As an example, geotextiles are used to prevent soil particles from migrating and infiltrating drainage aggregates or drainage pipes, while maintaining the normal operation of drainage systems, laying geotextiles under a riprap protective layer and other protective materials on coasts and riverbanks can prevent soil erosion and river bank collapse.
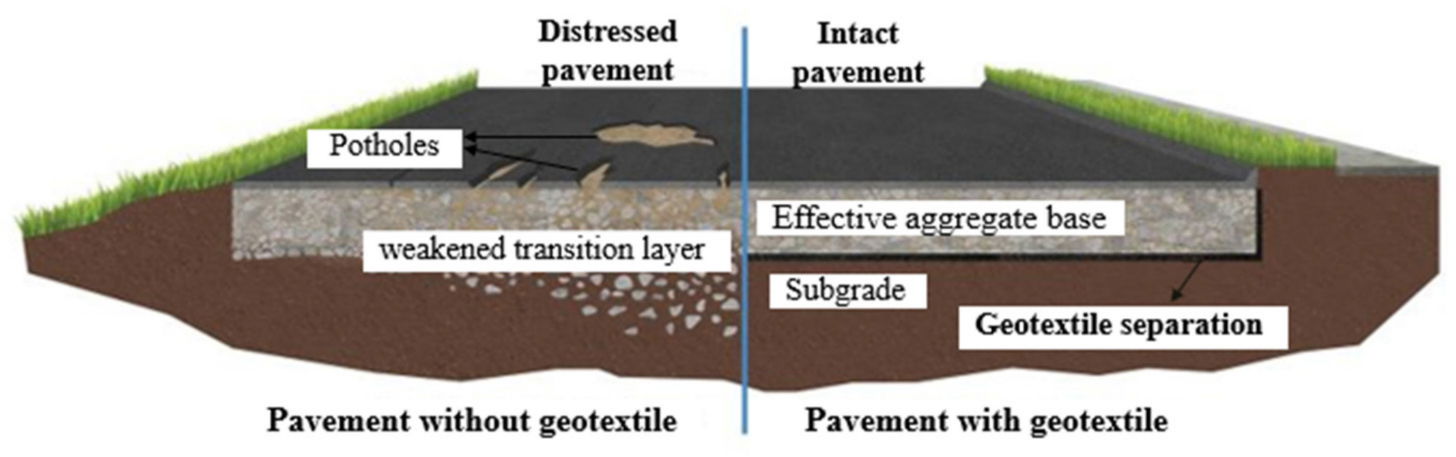
The above figure demonstrates the comparison of pavement with or without geotextiles. The separation function of geotextiles can effectively prevent the pumping effect created by dynamics. Some of the applications areas are :
- Between subgrade and stone base in unpaved and paved roads and airfields
- Between subgrade in railroads
- Between landfills and stone base courses
- Between geomembranes and sand drainage layers
- Beneath sidewalks slabs
- Beneath curb areas
- Beneath parking lots
- Beneath sport and athletic fields
Drainage
Geotextiles have favorable water conductivity, which are used as drainage channel. The water in the soil structure in the geotextiles can be collected and slowly discharged along the geotextiles. At present, geotextiles have been widely used in underground drainage, subgrade drainage, retaining wall drainage, and other drainage works.

Features
- They are lighter in weight, this makes for easier handling and laying on site.
- Transport and labour costs are less in real terms.
- Knitted geotextiles have a high tear strength.
- Good resistance to installation abuse
- Excellent performance strength for a wide range of roadway applications
- Chemically stable in a wide range of aggressive environments
- Cost effective
Applications
- Parking Lots
- Sludge Management
- Playground Construction
- Riverside & Coal Works
- Railway Works
- Road Works
